Mouse IFNAR1 / IFNAR Protein (His Tag)
CD118,Ifar,Ifnar,Ifrc,Infar
- 100ug (NPP2728) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50469-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD118,Ifar,Ifnar,Ifrc,Infar |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse IFNAR1 consists of 414 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 47 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm IFNAR1 is approximately 55-60 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 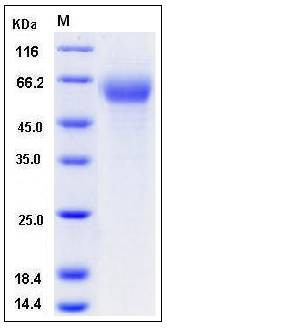 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse IFNAR1 (NP_034638.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Thr 429) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit mIFNB1-mediated protection of L929 mouse fibroblast cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) to viral lysis. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.2-1μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Cytokines / Chemokines in Angiogenesis |Interferons |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interferon-alpha/beta receptor alpha chain (IFNAR1) is a type I membrane protein that forms one of the two chains of a receptor for interferons alpha and beta. Binding and activation of the receptor stimulates Janus protein kinases, which in turn phosphorylate several proteins, including STAT1 and STAT2. The encoded protein also functions as an antiviral factor. Tyk2 slows down IFNAR1 degradation and that this is due, at least in part, to inhibition of IFNAR1 endocytosis. Mutant versions of IFNAR1, in which Tyr466 is changed to phenylalanine, can act in a dominant negative manner to inhibit phosphorylation of STAT2. These observations are consistent with a model in which IFNAR1 mediates the interaction between JAK kinases and the STAT transcription factors. |
| Reference |
