Mouse Gremlin 1 / GREM1 Protein (His Tag)
Cktsf1b1,Drm,Grem,ld
- 100ug (NPP1303) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50016-M08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | Cktsf1b1,Drm,Grem,ld |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse GREM1 consists of 171 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 19.7 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 25 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Lys 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 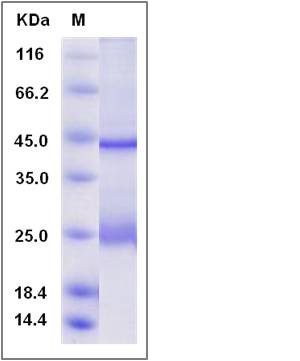 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse GREM1 (O70326) (Met1-Asp184) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit recombinant human BMP4-induced alkaline phosphatase production by MC3T3-E1 cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 1-7 μg/mL in the presence of 50 ng/mL of recombinant human BMP4. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Organogenesis |Skeletal development |Bone |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly, 0.5mM EDTA, 3mM DTT 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | GREM1 belongs to the DAN family. It contains 1 CTCK (C-terminal cystine knot-like) domain. GREM1 is a cysteine knot-secreted protein and acts as an inhibitor in the TGF beta signaling pathway. It inhibits BMP-2, -4, and -7. Inhibition by grem 1 of BMPs in mice allow the expression of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) 4 and 8 and Sonic hedgehog (SHH) which are necessary for proper limb development. It interacts with SLIT1 and SLIT2 in a glycosylation-dependent manner. As a cytokine, GREM1 may play an important role during carcinogenesis and metanephric kidney organogenesis, as a BMP antagonist required for early limb outgrowth and patterning in maintaining the FGF4-SHH feedback loop. It down-regulates the BMP4 signaling in a dose-dependent manner. It also acts as inhibitor of monocyte chemotaxis. GREM1 is highly expressed in small intestine, fetal brain and colon. |
| Reference |
